Cache memory is an important component in computer systems, crucial for ensuring efficient performance. When you’re using your computer, particularly with resource-heavy applications, understanding what cache memory is and how to manage it can significantly improve your system’s performance.
What is Cache Memory?
Cache memory, often referred to as CPU cache, is a type of high-speed volatile computer memory that provides high-speed data access to the processor. It is a smaller, faster memory, located closer to a processor core, which stores copies of the data from frequently used main memory locations. Here are the key aspects to understand:
1. Purpose
Speed Enhancement: The primary purpose of cache memory is to reduce the time it takes to access data from the main memory (RAM). By storing frequently accessed data and instructions, cache memory allows the processor to retrieve this information quickly, thereby speeding up processing time.
2. Types of Cache Memory:
- L1 Cache: Located inside the CPU chip, it is the fastest type of cache with the least capacity.
- L2 Cache: This can be found inside or outside the CPU chip and is slower than L1 but has a larger capacity.
- L3 Cache: Shared among the cores of a processor, it is slower than L1 and L2 but has a larger capacity.
3. Functioning:
Storing Frequently Used Data: When the CPU needs to access data, it first checks whether the data is in the cache. If it is, this is known as a cache hit, and the data can be read from the cache, which is much faster. If the data is not in the cache (a cache miss), the CPU will fetch it from the main memory and store a copy in the cache for future access.
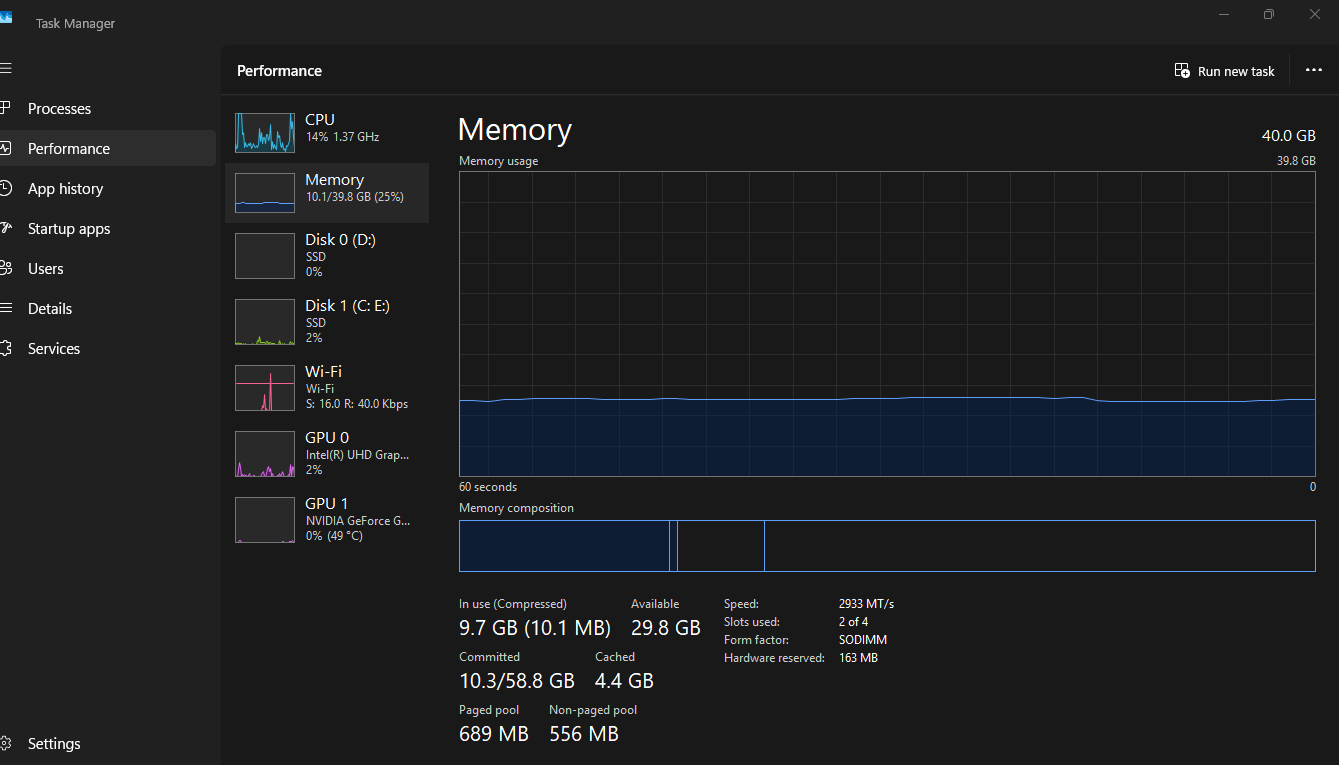
Cache Memory in Task Manager
When you open Task Manager, especially on Windows systems, you can see various performance metrics, including memory usage. Cache memory in this context is often part of the overall memory system designed to enhance performance.
1. Viewing Cache Memory:
- Accessing Task Manager: You can open Task Manager by pressing Ctrl + Shift + Esc or right-clicking on the taskbar and selecting Task Manager.
- Performance Tab: under the Performance tab, you’ll find detailed information about your memory usage. Here, you’ll see metrics like “Cached” memory, which indicates the amount of RAM being used to store frequently accessed data.
2. Impact on Performance:
- Improved Access Speed: Cached memory enhances the speed of data retrieval, leading to quicker application load times and smoother system performance.
- System Responsiveness: Efficient caching results in a more responsive system, as frequently used data is readily available.
How to Reduce Cache Memory
While cache memory is crucial for performance, there may be times when you need to manage or reduce it, especially if your system is experiencing performance issues. Here are some strategies:
1. Restart Your Computer:
- Clear Temporary Files: A simple restart can clear temporary files and reset cached memory, helping to improve performance.
- Refresh System Resources: Restarting your computer can refresh system resources, clearing the cache and freeing up memory.
2. Disk Cleanup:
- Built-in Utility: Use the built-in Disk Cleanup utility to remove temporary files and system cache. Access this by typing Disk Cleanup in the search bar and selecting the drive you want to clean.
- Clear System Cache: This tool allows you to delete temporary files, thumbnails, and system cache, freeing up memory.
3. Manage Startup Programs:
- Task Manager Settings: Open Task Manager, go to the Startup tab, and disable unnecessary programs that run at startup. This can reduce the amount of memory used by these programs, including cache memory.
- Selective Startup: Limit the number of programs that automatically start with your system to free up resources.
4. Optimize System Performance:
- Virtual Memory Settings: Adjust virtual memory settings by going to Control Panel > System > Advanced System Settings > Performance Settings > Advanced tab > Virtual Memory. Increasing the virtual memory size can help manage cache memory.
- ReadyBoost: Use ReadyBoost, a Windows feature that allows you to use a USB flash drive to improve system performance by adding additional cache memory.
5. Update and Maintain Software:
- Regular Updates: Keep your operating system and software up to date to benefit from performance improvements and bug fixes that can optimize memory usage.
- Driver Updates: Ensure your device drivers are updated to maintain efficient hardware performance and memory management.
6. Use Third-Party Tools:
- Memory Management Software: There are several third-party tools available that can help manage and optimize memory usage, such as CCleaner. These tools can clean up system cache and temporary files.
- Performance Monitoring: Use tools like Process Explorer to monitor and manage system performance, including memory and cache usage.
7. Upgrade Hardware:
- Increase RAM: Upgrading your system’s RAM can help reduce the reliance on cache memory, as more data can be stored directly in RAM.
- Faster Storage: Consider upgrading to a faster SSD, which can improve overall system performance and reduce the need for extensive caching.
Conclusion
Understanding cache memory and how to manage it is crucial for maintaining optimal system performance. Cache memory plays a vital role in speeding up data access and improving system responsiveness. However, if your system is experiencing performance issues, managing and reducing cache memory can help.